Vibrio cholerae
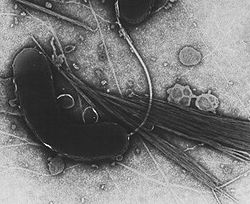
Vibrio cholerae(also Kommabacillus) is a gram negative comma-shaped bacterium with a polar flagellum that causes cholera in humans.[1][2] V. cholerae and other species of the genus Vibrio belong to the gamma subdivision of the Proteobacteria. There are two major biotypes of V. cholerae, classical and El Tor, and numerous serogroups.
V. cholerae was first isolated as the cause of cholera by Italian anatomist Filippo Pacini in 1854, but his discovery was not widely known until Robert Koch, working independently thirty years later, publicized the knowledge and the means of fighting the disease.[3][4]
Genomics and Evolution
The 4.0 Mbp genome of N16961, an O1 serogroup, (in America) El Tor biotype, 7th pandemic strain of V. cholerae, is composed of two circular chromosomes of unequal size that are predicted to encode a total of 3,885 genes[5]. The genomic sequence of this representative strain has furthered our understanding of the genetic and phenotypic diversity found within the species V. cholerae. Sequence data have been used to identify horizontally acquired sequences, dissect complex regulatory and signaling pathways, and develop computational approaches to predict patterns of gene expression and the presence of metabolic pathway components. Microarrays are being used to study the evolution of the organism. Genomic sequencing of additional strains, subtractive hybridization studies, and the introduction of new model systems have also contributed to the identification of novel sequences and pathogenic mechanisms associated with other strains.[2].
See also
References
External links
|
Cholera |
|
| Cholera |
|
 |
|
| Cholera Bacteria |
Vibrio cholerae - Strains: El Tor
Discovery:1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak - John Snow - Reverend Henry Whitehead |
|
| Treatment |
|
|
| Outbreaks |
Cholera Pandemics: First cholera pandemic - Second cholera pandemic - Third cholera pandemic - Fourth cholera pandemic - Fifth cholera pandemic - Sixth cholera pandemic - Seventh cholera pandemic
1854 Broad Street cholera outbreak - 2007 Central Luzon hog cholera outbreak - 2007 Iraq cholera outbreak - 2008 Congo cholera outbreak - 2008–2009 Zimbabwean cholera outbreak - 2010 Haiti cholera outbreak
|
|
|
|
|
gr+f/gr+a(t)/gr-p(c)/gr-o
|
|
|
|
|
|
Infectious diseases · Bacterial diseases: Proteobacterial G- (primarily A00–A79, 001–041, 080–109) |
|
| α |
|
Rickettsiales
|
|
Rickettsiaceae/
(Rickettsioses)
|
|
|
Rickettsia typhi (Murine typhus) · Rickettsia prowazekii (Epidemic typhus, Brill–Zinsser disease, Flying squirrel typhus)
|
|
|
Spotted
fever
|
|
Tick-borne
|
Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain spotted fever) · Rickettsia conorii (Boutonneuse fever) · Rickettsia japonica (Japanese spotted fever) · Rickettsia sibirica (North Asian tick typhus) · Rickettsia australis (Queensland tick typhus) · Rickettsia honei (Flinders Island spotted fever) · Rickettsia africae (African tick bite fever) · Rickettsia parkeri (American tick bite fever) · Rickettsia aeschlimannii (Rickettsia aeschlimannii infection)
|
|
|
|
Rickettsia akari (Rickettsialpox) · Orientia tsutsugamushi (Scrub typhus)
|
|
|
|
Rickettsia felis (Flea-borne spotted fever)
|
|
|
|
|
Anaplasmataceae
|
Ehrlichiosis: Anaplasma phagocytophilum (Human granulocytic anaplasmosis, Anaplasmosis) · Ehrlichia chaffeensis (Human monocytic ehrlichiosis) · Ehrlichia ewingii (Ehrlichiosis ewingii infection)
|
|
|
|
Rhizobiales
|
|
Brucellaceae
|
|
|
|
Bartonellaceae
|
Bartonellosis: Bartonella henselae (Cat scratch disease) · Bartonella quintana (Trench fever) · either henselae or quintana (Bacillary angiomatosis) · Bartonella bacilliformis (Carrion's disease, Verruga peruana)
|
|
|
|
| β |
|
Neisseriales
|
M+ Neisseria meningitidis/meningococcus (Meningococcal disease, Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, Meningococcal septicaemia)
M- Neisseria gonorrhoeae/gonococcus (Gonorrhea)
ungrouped: Eikenella corrodens/ Kingella kingae (HACEK) · Chromobacterium violaceum (Chromobacteriosis infection)
|
|
|
Burkholderiales
|
Burkholderia pseudomallei (Melioidosis) · Burkholderia mallei (Glanders) · Burkholderia cepacia complex · Bordetella pertussis/Bordetella parapertussis ( Pertussis)
|
|
|
| γ |
|
Enterobacteriales
(OX-)
|
|
Lac+
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae (Rhinoscleroma, Klebsiella pneumonia) · Klebsiella granulomatis (Granuloma inguinale) · Klebsiella oxytoca
Escherichia coli: Enterotoxigenic · Enteroinvasive · O157:H7/Enterohemorrhagic (Hemolytic-uremic syndrome)
Enterobacter aerogenes/Enterobacter cloacae
|
|
|
Slow/weak
|
Serratia marcescens (Serratia infection) · Citrobacter koseri/Citrobacter freundii
|
|
|
Lac-
|
|
H2S+
|
Salmonella enterica ( Typhoid fever, Paratyphoid fever, Salmonellosis)
|
|
|
H2S-
|
Shigella dysenteriae/sonnei/flexneri/boydii (Shigellosis, Bacillary dysentery) · Proteus mirabilis/ Proteus vulgaris · Yersinia pestis ( Plague/ Bubonic plague) · Yersinia enterocolitica · Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
|
|
|
|
|
Pasteurellales
|
Haemophilus: H. influenzae (Haemophilus meningitis, Brazilian purpuric fever) · H. ducreyi (Chancroid) H. parainfluenzae (HACEK)
Pasteurella multocida (Pasteurellosis) · Actinobacillus (Actinobacillosis)
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (HACEK)
|
|
|
Legionellales
|
|
|
|
Thiotrichales
|
Francisella tularensis (Tularemia)
|
|
|
Vibrionales
|
Vibrio cholerae ( Cholera) · Vibrio vulnificus · Vibrio parahaemolyticus · Vibrio alginolyticus · Plesiomonas shigelloides
|
|
|
Pseudomonadales
|
|
|
|
Xanthomonadales
|
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
|
|
|
Cardiobacteriales
|
Cardiobacterium hominis (HACEK)
|
|
|
Aeromonadales
|
Aeromonas hydrophila/Aeromonas veronii (Aeromonas infection)
|
|
|
| ε |
|
|
|
|
|
gr+f/gr+a(t)/gr-p(c)/gr-o
|
|
|
|
|
